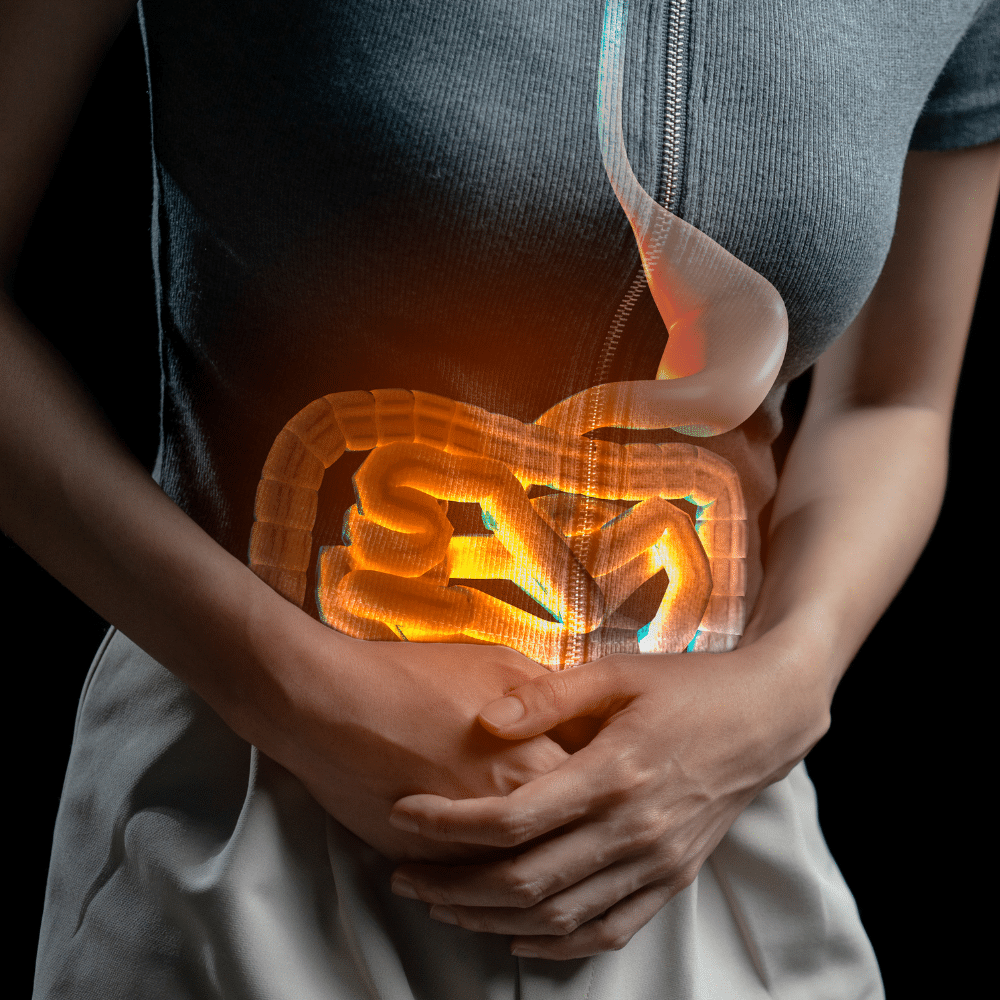
Are you experiencing abdominal pain?
Uncover the Root Causes and Find Relief
Abdominal pain is a common ailment that can range from mild discomfort to severe agony, and it affects people of all ages. It is essential to understand the causes and symptoms of abdominal pain to effectively address and manage it.
The causes of abdominal pain are varied and include digestive issues, infections, inflammation, and organ problems. The symptoms can be very different and depend on the underlying cause. Some common symptoms include cramping in the lower abdomen, bloating, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and a feeling of fullness.
What is Abdominal Pain?
Abdominal pain is a common ailment that can range from mild discomfort to severe agony in the belly region.
Common Symptoms
- Cramping
- Bloating
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- A feeling of fullness

Common Causes
- Digestive Issues
- Unhealthy Eating Patterns
- Infections
- Inflammation
How to Manage Abdominal Pain
Microbiome testing
If you’re experiencing extreme abdominal pain, try gut-health testing to determine the root cause.
Managing Stress
Managing stress can also be helpful, as stress can trigger abdominal pain in some people.
Eating a healthy diet
Identifying and avoiding foods that trigger stomach pain, such as spicy or fatty foods, can help prevent discomfort and inflammation in the digestive system.
Exercising Regularly
Engaging in regular physical exercise can help promote healthy digestion and reduce the risk of abdominal pain.
Taking probiotics
New research suggests that probiotics may be a great option for helping abdominal pain over time.
Relieving Abdominal Pain
Heat Therapy
Applying a heating pad or warm compress to the abdomen can help relax the muscles and provide temporary relief from abdominal pain.
Over-The-Counter Remedies
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help alleviate mild to moderate abdominal pain.
Rest and Relaxation
Engaging in activities that promote relaxation, such as deep breathing exercises, yoga, or meditation, can help reduce stress and alleviate abdominal pain.
Hydration
Drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day can help prevent dehydration and promote healthy digestion, reducing the risk of abdominal pain.
Watch this video to learn more about indigestion
Fix Your Abdominal Health
Abdominal pain can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and indicators is crucial for effectively addressing and managing pain. Managing and treating abdominal pain at home can be possible with simple remedies and lifestyle changes, but it is important to consult a healthcare professional for severe or persistent pain. The role of probiotics in alleviating stomach pain and supporting a healthy gut microbiome should not be overlooked. By incorporating probiotic-rich foods and making dietary modifications, individuals can potentially reduce abdominal pain and promote digestive health. Implementing lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, avoiding trigger foods, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying hydrated, can further prevent and reduce stomach pain. By taking control of your abdominal pain and seeking professional help when necessary, you can improve your overall well-being and quality of life.
If you are experiencing severe or persistent abdominal pain, please consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and advice.
Sources
[1] Pusceddu, M. M., & Gareau, M. G. (2018). Visceral pain: gut microbiota, a new hope?. Journal of biomedical science, 25(1), 73. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-018-0476-7
[2] Shaikh, S. D., Sun, N., Canakis, A., Park, W. Y., & Weber, H. C. (2023). Irritable Bowel Syndrome and the Gut Microbiome: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of clinical medicine 12(7): 2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072558
[3] Ruben A.T., et al., (2020). Longitudinal Multi-omics Reveals Subset-Specific Mechanisms Underlying Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Cell, 182(6), 1460-1473.e17, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.007.
[4] Gordon M, Wallace C, Sinopoulou V, Akobeng AK. Probiotics for management of functional abdominal pain disorders in children. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2023, Issue 2. Art. No.: CD012849. https://doi.org//10.1002/14651858.CD012849.pub2
[5] Hungin, A. P. S., European Society for Primary Care Gastroenterology, et al., (2018). Systematic review: probiotics in the management of lower gastrointestinal symptoms – an updated evidence-based international consensus. Alimentary pharmacology & therapeutics, 47(8), 1054–1070. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.14539
https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/abdominal-pain/basics/causes/sym-20050728
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/4167-abdominal-pain
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003120.htm
https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/abdominal-pain
https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/abdominal-pain-causes-treatments
https://www.healthline.com/health/abdominal-pain
https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/probiotics-risks-benefits