In recent years, the conversation around nutrition has intensely focused on the role different types of fats play in our overall health. Among these, saturated fat has been a topic of considerable debate, particularly concerning its impact on gut health. As we continue to explore the complex relationship between diet and the gut microbiome, understanding how saturated fat affects this dynamic ecosystem is essential. The journey to understanding saturated fat and its implications for gut health is not just about eliminating or consuming certain foods; it’s about striking a balance that supports a healthy microbiome and, consequently, a healthier you. This article aims to unravel the intricate effects of saturated fat on gut health and provide practical insights to help you make informed dietary choices.
Understanding Saturated Fat: What Is It?
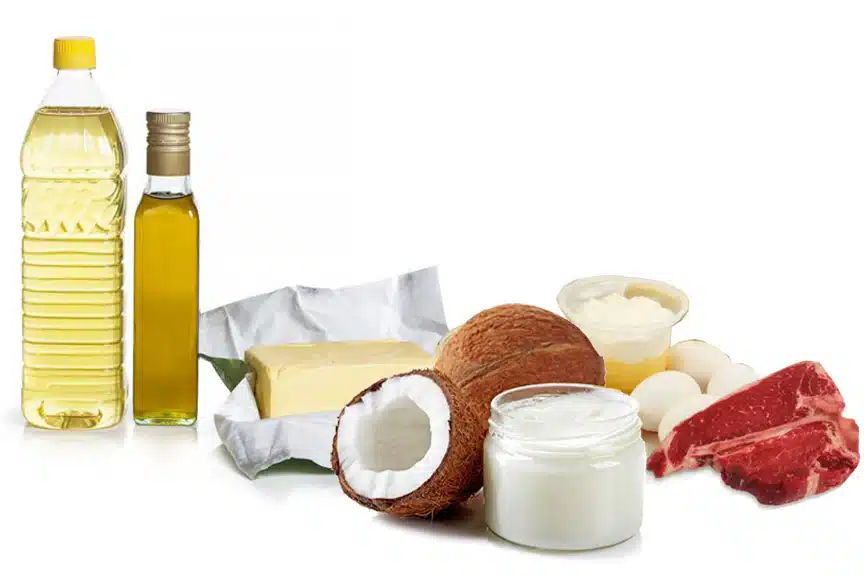
Saturated fats are a type of dietary fat found predominantly in animal products such as meat, butter, and dairy, as well as certain plant oils like coconut and palm oil. Chemically, saturated fats are distinguished by their lack of double bonds between carbon molecules, which makes them solid at room temperature. This structural simplicity is often contrasted with unsaturated fats, which have one or more double bonds and are usually liquid at room temperature.
For decades, saturated fats have been scrutinized for their association with heart disease and other chronic conditions. However, recent research suggests that the effects of saturated fats may be more nuanced than previously thought. While they can potentially raise low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels, some studies indicate that not all saturated fats have the same impact on cardiovascular health.
Understanding the role of saturated fats in our diet requires a comprehensive view that considers both their potential risks and benefits. This balanced perspective is crucial when evaluating their effects, not just on cardiovascular health but also on the gut microbiome—a key player in overall health.
Effects of Saturated Fat on Gut Health
The effects of saturated fat on gut health are a subject of ongoing research, with studies exploring how these fats influence the gut microbiome [1-3]. Saturated fats, like other dietary components, can alter the composition and activity of this microbial community. One of the primary concerns with high saturated fat intake is its potential to disrupt the balance of gut bacteria. Some research indicates that diets rich in saturated fats can lead to an increase in harmful bacteria, which may contribute to inflammation and other gut-related issues. This disruption could potentially affect the gut barrier, making it more permeable and leading to a condition commonly referred to as “leaky gut.”[4]
However, it’s essential to recognize that the relationship between saturated fats and gut health is not entirely negative. Certain types of saturated fats may have neutral or even beneficial effects, depending on the overall dietary context and the individual’s existing gut microbiome. Understanding these nuances is key to making dietary choices that support gut health.
The Impact of Saturated Fat on the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome’s response to saturated fat can vary significantly based on factors such as the type of fat, the overall diet, and individual differences in microbiome composition. Some studies suggest that diets high in saturated fats could lead to a decrease in microbial diversity, which is often associated with negative health outcomes [1,2,4]. A diverse microbiome is generally considered healthier as it can better withstand disruptions and perform a broader range of functions.
Additionally, saturated fats may influence the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) by gut bacteria. SCFAs, such as butyrate, are crucial for maintaining gut health as they serve as an energy source for colon cells and have anti-inflammatory properties. A diet rich in saturated fats might alter the types and amounts of SCFAs produced, potentially affecting gut health [3,4].
However, it’s worth noting that not all saturated fats are created equal. Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), a type of saturated fat found in coconut oil, have been shown to have different effects on the gut microbiome compared to long-chain saturated fats. MCTs may promote the growth of beneficial bacteria and increase SCFA production, highlighting the importance of considering the type of saturated fat in dietary assessments [5].
Pros of Saturated Fat on Gut Health
While saturated fat often gets a bad rap, there are potential benefits associated with its consumption, particularly in moderation and as part of a balanced diet. These benefits are often context-dependent and can vary based on individual health needs and dietary patterns.
- Energy Source: Saturated fats are a dense source of energy, which can be beneficial for individuals who require higher calorie intakes, such as athletes or those with high energy demands.
- Nutrient Absorption: Certain vitamins, such as A, D, E, and K, are fat-soluble, meaning they require the presence of dietary fat for optimal absorption. Including moderate amounts of saturated fat in the diet can enhance the uptake of these essential nutrients.
- Gut Microbiome Diversity: Some research suggests that specific types of saturated fats, like MCTs, may support a diverse and resilient gut microbiome [5]. This diversity is crucial for maintaining a healthy gut environment.
While there are potential benefits, it’s crucial to consume saturated fats in moderation and as part of a diet that includes a variety of other nutrients. Balancing these fats with other healthy dietary components can help ensure that the benefits are maximized without increasing health risks.
Cons of Saturated Fat on Gut Health
Despite some potential benefits, there are also notable drawbacks to high saturated fat consumption, especially when it comes to gut health. These cons are often highlighted in research exploring the effects of saturated fat on the gut microbiome and overall health.
- Increased Inflammation: High intake of saturated fats may lead to an increase in pro-inflammatory compounds in the gut, which can exacerbate inflammatory conditions and impact overall gut health [1].
- Reduced Microbial Diversity: Diets rich in saturated fats have been associated with a decrease in gut microbiome diversity, which can weaken the gut’s resilience to harmful pathogens and disrupt normal gut functions.
- Altered Gut Barrier Function: Excessive saturated fat consumption may compromise the integrity of the gut barrier, leading to increased permeability [4].
Considering these cons, it’s important to approach saturated fat consumption with awareness and moderation. Understanding these potential drawbacks can help us make informed choices that support both gut health and overall well-being.
Balancing Saturated Fat in Your Diet
Achieving a balance of saturated fats in your diet is crucial for maintaining gut health while reaping their potential benefits. Here are some practical strategies to help you manage saturated fat intake effectively:
- Diversify Your Fats: Include a variety of fats in your diet, such as unsaturated fats from sources like olive oil, nuts, and avocados. This can help balance the effects of saturated fats and provide a broader range of nutrients.
- Portion Control: Moderation is key. Keep an eye on portion sizes, especially when consuming high-fat foods like cheese, butter, and fatty meats.
- Incorporate Fiber-Rich Foods: Fiber from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help mitigate some of the negative effects of saturated fats by promoting gut health and supporting a diverse microbiome.
By being mindful of these strategies, we can enjoy the potential benefits of saturated fats without compromising our gut health.
Practical Tips for a Gut-Healthy Diet
Maintaining a gut-healthy diet involves more than just managing saturated fat intake; it’s about creating a balanced dietary pattern that supports overall health. Here are some practical tips to help you achieve this:
- Include Probiotics and Prebiotics: Foods rich in probiotics, like yogurt and fermented vegetables, can enhance gut health. Similarly, prebiotics found in foods like garlic, onions, and bananas feed beneficial gut bacteria.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining a healthy gut environment and supporting digestion.
- Limit Processed Foods: Processed foods often contain unhealthy fats and additives that can negatively impact gut health.
By incorporating these tips into your daily routine, you can support a healthy gut microbiome and improve your overall health.
Final Thoughts
As we wrap up our exploration of saturated fat and its effects on gut health, it’s clear that understanding and managing the role of these fats in our diet is crucial. While saturated fats can have both positive and negative impacts, the key lies in moderation and balance. The best way to do this is to strive for a balanced dietary approach that includes a variety of fats, fibers, and nutrients to support gut health and overall wellness.
It’s also important to stay informed about the latest research on saturated fats and their effects on the gut microbiome to make educated dietary decisions while recognizing that individual responses to saturated fats can vary, and tailor your diet to meet your unique health needs. By keeping these takeaways in mind, we can navigate the complexities of saturated fat and gut health, ensuring that our dietary choices promote a healthy microbiome and a healthier life.
Sources
[1] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5083795/
[2] https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-41074-3
[3] https://gut.bmj.com/content/68/8/1417
[4] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7664638/
[5] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4882694/
https://flore.com/blogs/learn/saturated-fats-impacts-your-gut?
https://www.uclahealth.org/news/article/eating-healthy-fats-has-many-benefits
https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/the-truth-about-fats-bad-and-good